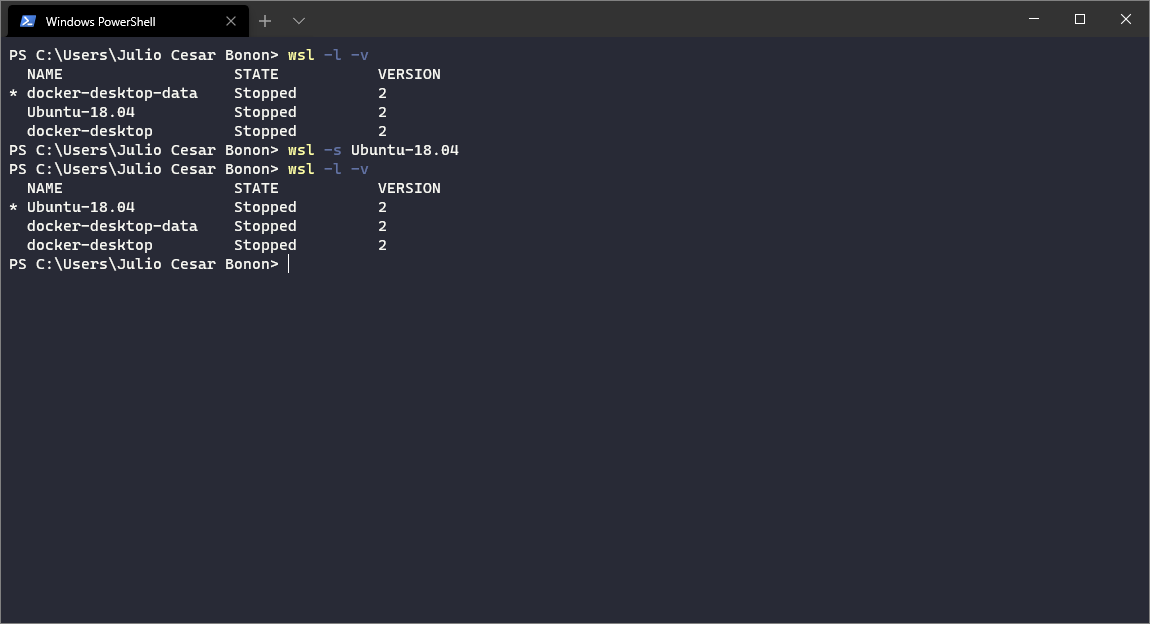
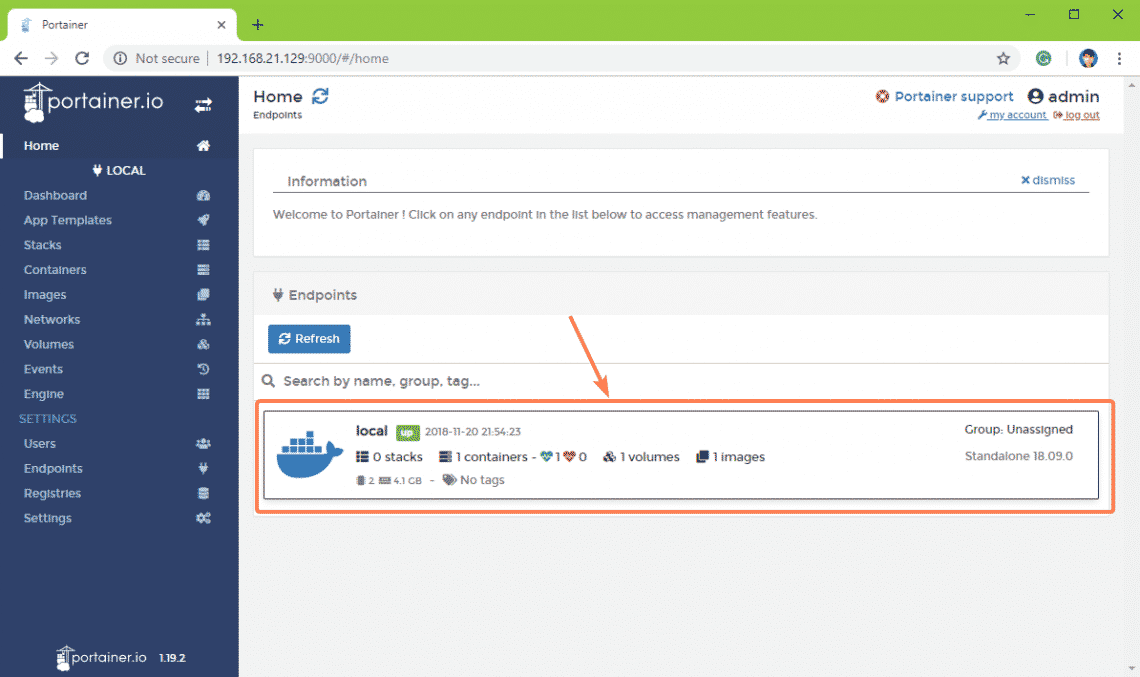
In this tutorial, I will show you step-by-step how to install and configure Portainer on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. We will install and configure Portainer, deploy the Apps Container, Manage Container, images, network, and volumes for our Docker environment. Ubuntu Server 16.04; Root privileges; What we will do. Install Docker on Ubuntu 16.04. We wrote a number of LinuxKit components, used both in our Hyper-V and Mac VMs: services controlling the lifecycle of Docker and Kubernetes, services to collect diagnostics in case of failure, services aggregating logs, etc. Those services are packaged in an iso file in the Docker Desktop installation directory (docker-desktop.iso).
Today we are delighted to introduce the new Minimal Ubuntu, optimized for automated use at scale, with a tiny package set and minimal security cross-section. Speed, performance and stability are primary concerns for cloud developers and ops.
'The small footprint of Minimal Ubuntu, when deployed with fast VM provisioning from GCE, helps deliver drastically improved boot times, making them a great choice for developers looking to build their applications on Google Cloud Platform,' said Paul Nash, Group Product Manager, Google Cloud.'
Smaller and faster, for automated cloud operations
Minimal Ubuntu is the smallest Ubuntu base image for your cloud operations. These images are less than 50% the size of the standard Ubuntu server image, and boot up to 40% faster. Images of Minimal Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and 18.04 LTS are available for use now in Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine (GCE), LXD and KVM/OpenStack.
Tiny container base image
The 29MB Docker image for Minimal Ubuntu 18.04 LTS serves as a highly efficient container starting point, and allows developers to deploy multicloud containerized applications faster. For modern Docker workflows with Kubernetes, the minimal Ubuntu image provides a balance of compatibility, familiarity, performance and size. This is the standard Ubuntu 18.04 LTS image on the Docker Hub.
Cloud images also contain the optimised kernel for each cloud and supporting boot utilities.
Fully compatible with all Ubuntu packages
While the footprint of Minimal Ubuntu is greatly reduced, it preserves full compatibility with standard Ubuntu operations. Any Ubuntu package can be installed on Minimal Ubuntu. Get exactly the image you need by simply adding your required packages, with dependencies, to a Minimal Ubuntu base image.
Minimal Ubuntu is designed for completely automated operations, with none of the usual human-friendly utilities for comfortable interactive usage. Editors, documentation, locales and other user-oriented features of Ubuntu Server have been removed. What remains are only the vital components of the boot sequence. Images still contain ssh, apt and snapd so you can connect and install any package you're missing. The unminimize tool lets you ‘rehydrate' your image into a familiar Ubuntu server package set, suitable for command line interaction.
Optimized for cloud hypervisors
Minimal Ubuntu uses the optimized kernels on Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud. The downloadable Minimal Ubuntu image ships with a KVM-optimised kernel and tuned for boot speed and size.
Minimized security cross-section
With fewer installed packages, Minimal Ubuntu images will avoid some security vulnerabilities and require fewer updates over time. Use of Minimal Ubuntu will reduce overall bandwidth consumption for an institution and require less storage.
Download for private clouds, published on public clouds
Minimal Ubuntu images for private clouds are available for download at http://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/minimal/releases/
Minimal Ubuntu images are available on AWS and Google Cloud.
On AWS, see the listing of minimal images at US-WEST 2 minimal images
Docker Desktop For Ubuntu Installer
and on Google Cloud use the SDK CLI with:
Using Minimal Images from Dockerhub
Docker Desktop For Ubuntu Operating System
On Dockerhub, the new Ubuntu 18.04 LTS image is now the new Minimal Ubuntu 18.04 image. Launching a Docker instance with docker run ubuntu:18.04 therefore launches a Docker instance with the latest Minimal Ubuntu.
Talk to us today
Docker Desktop For Ubuntu 16.04
Interested in running Ubuntu in your organisation?
Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend has now been available for a few months for Windows 10 insider users and Microsoft just released WSL 2 on the Release Preview channel (which means GA is very close). We and our early users have accumulated some experience working with it and are excited to share a few best practices to implement in your Linux container projects!
Docker Desktop with the WSL 2 backend can be used as before from a Windows terminal. We focused on compatibility to keep you happy with your current development workflow.
But to get the most out of Windows 10 2004 we have some recommendations for you.
Fully embrace WSL 2
The first and most important best practice we want to share, is to fully embrace WSL 2. Your project files should be stored within your WSL 2 distro of choice, you should run the docker CLI from this distro, and you should avoid accessing files stored on the Windows host as much as possible.
For backward compatibility reasons, we kept the possibility to interact with Docker from the Windows CLI, but it is not the preferred option anymore.
Running docker CLI from WSL will bring you…
Awesome mounts performance
Both your own WSL 2 distro and docker-desktop run on the same utility VM. They share the same Kernel, VFS cache etc. They just run in separate namespaces so that they have the illusion of running totally independently. Docker Desktop leverages that to handle bind mounts from a WSL 2 distro without involving any remote file sharing system. This means that when you mount your project files in a container (with docker run -v ~/my-project:/sources <...>), docker will propagate inotify events and share the same cache as your own distro to avoid reading file content from disk repeatedly.
A little warning though: if you mount files that live in the Windows file system (such as with docker run -v /mnt/c/Users/Simon/windows-project:/sources <...>), you won't get those performance benefits, as /mnt/c is actually a mountpoint exposing Windows files through a Plan9 file share.
Compatibility with Linux toolchains and build scripts
Most reasonably sized projects involving Linux containers come with a bunch of automation scripts. Those scripts are often developed for Linux first (because most of the time, CI/CD pipelines for those projects run on Linux), and developers running on Windows are often considered second-class citizens. They are often using less polished versions of those scripts, and have to deal with subtle behavioral differences.
By fully embracing WSL 2, Windows developers can use the exact same build and automation scripts as on Linux. This means that Windows-specific scripts don't need to be maintained anymore. Also, that means that you won't experience issues with different line endings between Windows and Mac/Linux users!
What about my IDE?
If you want an IDE for editing your files, you can do that even if they are hosted within your WSL 2 distro. There are 3 different ways:
- Use Visual Studio Code Remote to WSL extension
If your IDE is Visual Studio Code, using Remote to WSL is the best way to continue working on your project. Visual Studio Code architecture is based on a client/server approach where pretty much everything except rendering and input processing is done in a server process, while the UI itself runs in a client process. Remote to WSL leverages that to run the whole server process within WSL while the UI runs as a classic win32 process.
That means that you get the same experience as before, but all your language services, terminals etc. run within WSL.
For more information, see Microsoft's VS Code Remote to WSL documentation.
- Point your IDE to your distro network share
WSL provides a network share for each of your running distros. For example, if I have a project in my Ubuntu distro at `~/wall-e`, I can access it from Windows Explorer (and from any Windows Process) via the special network share `wsl$Ubuntuhomesimonwall-e`.
- Run an X11 server on Windows, and run a Linux native IDE
The setup is a bit more complicated, but you always have the possibility to run an X11 server on Windows (VcXsrv, X410,…) and configure your DISPLAY environment variable such that GUI apps on Linux get rendered properly.
Use BuildKit and multi-stage builds
Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend has access to all your CPU cores. To leverage this as much as possible (and also to get access to the latest build features), you should enable BuildKit by default.
The easiest way to do that is to add the following line to your ~/.profile file:
export DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1.
This way, anytime you run docker build, it will run the build with the awesome BuildKit which is capable of running different build stages concurrently.
Use resource limits
Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend can use pretty much all CPU and memory resources on your machine. This is awesome for most cases, but there is a category of workloads where this can cause issues. Indeed, some containers (mainly databases, or caching services) tend to allocate as much memory as they can, and leave other processes (Linux or Win32) starving. Docker provides a way to impose limits in allocatable memory (as well as quotas on CPU usage) by a container. You can find documentation about it here: https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/resource_constraints/.
Reclaim cached memory
WSL 2 automatically reclaims memory when it is freed, to make it available to Windows processes. However, if the kernel decides to keep content in cache (and with Docker, it tends to happen quite a lot), the amount of memory reclaimed might not be sufficient.
Fully compatible with all Ubuntu packages
While the footprint of Minimal Ubuntu is greatly reduced, it preserves full compatibility with standard Ubuntu operations. Any Ubuntu package can be installed on Minimal Ubuntu. Get exactly the image you need by simply adding your required packages, with dependencies, to a Minimal Ubuntu base image.
Minimal Ubuntu is designed for completely automated operations, with none of the usual human-friendly utilities for comfortable interactive usage. Editors, documentation, locales and other user-oriented features of Ubuntu Server have been removed. What remains are only the vital components of the boot sequence. Images still contain ssh, apt and snapd so you can connect and install any package you're missing. The unminimize tool lets you ‘rehydrate' your image into a familiar Ubuntu server package set, suitable for command line interaction.
Optimized for cloud hypervisors
Minimal Ubuntu uses the optimized kernels on Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud. The downloadable Minimal Ubuntu image ships with a KVM-optimised kernel and tuned for boot speed and size.
Minimized security cross-section
With fewer installed packages, Minimal Ubuntu images will avoid some security vulnerabilities and require fewer updates over time. Use of Minimal Ubuntu will reduce overall bandwidth consumption for an institution and require less storage.
Download for private clouds, published on public clouds
Minimal Ubuntu images for private clouds are available for download at http://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/minimal/releases/
Minimal Ubuntu images are available on AWS and Google Cloud.
On AWS, see the listing of minimal images at US-WEST 2 minimal images
Docker Desktop For Ubuntu Installer
and on Google Cloud use the SDK CLI with:
Using Minimal Images from Dockerhub
Docker Desktop For Ubuntu Operating System
On Dockerhub, the new Ubuntu 18.04 LTS image is now the new Minimal Ubuntu 18.04 image. Launching a Docker instance with docker run ubuntu:18.04 therefore launches a Docker instance with the latest Minimal Ubuntu.
Talk to us today
Docker Desktop For Ubuntu 16.04
Interested in running Ubuntu in your organisation?
Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend has now been available for a few months for Windows 10 insider users and Microsoft just released WSL 2 on the Release Preview channel (which means GA is very close). We and our early users have accumulated some experience working with it and are excited to share a few best practices to implement in your Linux container projects!
Docker Desktop with the WSL 2 backend can be used as before from a Windows terminal. We focused on compatibility to keep you happy with your current development workflow.
But to get the most out of Windows 10 2004 we have some recommendations for you.
Fully embrace WSL 2
The first and most important best practice we want to share, is to fully embrace WSL 2. Your project files should be stored within your WSL 2 distro of choice, you should run the docker CLI from this distro, and you should avoid accessing files stored on the Windows host as much as possible.
For backward compatibility reasons, we kept the possibility to interact with Docker from the Windows CLI, but it is not the preferred option anymore.
Running docker CLI from WSL will bring you…
Awesome mounts performance
Both your own WSL 2 distro and docker-desktop run on the same utility VM. They share the same Kernel, VFS cache etc. They just run in separate namespaces so that they have the illusion of running totally independently. Docker Desktop leverages that to handle bind mounts from a WSL 2 distro without involving any remote file sharing system. This means that when you mount your project files in a container (with docker run -v ~/my-project:/sources <...>), docker will propagate inotify events and share the same cache as your own distro to avoid reading file content from disk repeatedly.
A little warning though: if you mount files that live in the Windows file system (such as with docker run -v /mnt/c/Users/Simon/windows-project:/sources <...>), you won't get those performance benefits, as /mnt/c is actually a mountpoint exposing Windows files through a Plan9 file share.
Compatibility with Linux toolchains and build scripts
Most reasonably sized projects involving Linux containers come with a bunch of automation scripts. Those scripts are often developed for Linux first (because most of the time, CI/CD pipelines for those projects run on Linux), and developers running on Windows are often considered second-class citizens. They are often using less polished versions of those scripts, and have to deal with subtle behavioral differences.
By fully embracing WSL 2, Windows developers can use the exact same build and automation scripts as on Linux. This means that Windows-specific scripts don't need to be maintained anymore. Also, that means that you won't experience issues with different line endings between Windows and Mac/Linux users!
What about my IDE?
If you want an IDE for editing your files, you can do that even if they are hosted within your WSL 2 distro. There are 3 different ways:
- Use Visual Studio Code Remote to WSL extension
If your IDE is Visual Studio Code, using Remote to WSL is the best way to continue working on your project. Visual Studio Code architecture is based on a client/server approach where pretty much everything except rendering and input processing is done in a server process, while the UI itself runs in a client process. Remote to WSL leverages that to run the whole server process within WSL while the UI runs as a classic win32 process.
That means that you get the same experience as before, but all your language services, terminals etc. run within WSL.
For more information, see Microsoft's VS Code Remote to WSL documentation.
- Point your IDE to your distro network share
WSL provides a network share for each of your running distros. For example, if I have a project in my Ubuntu distro at `~/wall-e`, I can access it from Windows Explorer (and from any Windows Process) via the special network share `wsl$Ubuntuhomesimonwall-e`.
- Run an X11 server on Windows, and run a Linux native IDE
The setup is a bit more complicated, but you always have the possibility to run an X11 server on Windows (VcXsrv, X410,…) and configure your DISPLAY environment variable such that GUI apps on Linux get rendered properly.
Use BuildKit and multi-stage builds
Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend has access to all your CPU cores. To leverage this as much as possible (and also to get access to the latest build features), you should enable BuildKit by default.
The easiest way to do that is to add the following line to your ~/.profile file:
export DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1.
This way, anytime you run docker build, it will run the build with the awesome BuildKit which is capable of running different build stages concurrently.
Use resource limits
Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend can use pretty much all CPU and memory resources on your machine. This is awesome for most cases, but there is a category of workloads where this can cause issues. Indeed, some containers (mainly databases, or caching services) tend to allocate as much memory as they can, and leave other processes (Linux or Win32) starving. Docker provides a way to impose limits in allocatable memory (as well as quotas on CPU usage) by a container. You can find documentation about it here: https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/resource_constraints/.
Reclaim cached memory
WSL 2 automatically reclaims memory when it is freed, to make it available to Windows processes. However, if the kernel decides to keep content in cache (and with Docker, it tends to happen quite a lot), the amount of memory reclaimed might not be sufficient.
To reclaim more memory, after stopping your containers, you can run echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches as root to drop the kernel page cache and make WSL 2 reclaim memory used by its VM.
What next
We are excited for people to use Docker Desktop with WSL 2 and hope that the tips and tricks in this article will help you get the best performance for all of your workloads.
If you have another tip or idea you want to share with us for using Docker send us a tweet @docker or if you have feedback on our implementation then raise a ticket against our Github Repo.
